티스토리 뷰
[ProgrammingLanguage][WIP] Syntax(구문), Semantic(의미론) 이해하기
SweetDev 2021. 10. 5. 15:39이번 포스팅에서는 Chapter3를 다뤄보려고 한다!
Syntax(구문):
Semantic(의미론):
의미는 구문과 매우 밀접하다. 보고 유추할 수 있을 정도여야 한다!
용어 정리하기
- sentence: character로 구성된 문장
- language: sentence의 집합
- lexeme(어휘 항목): language의 가장 낮은 level의 syntatic unit (ex: *, sum, begin)
- token: lexeme의 한 분류 (ex: identifier)
예시)

Language란? 정의해보자!
크게 두가지 방식 - Recognizer(인식에 의한 정의) - parser같은거, Generator(생성에 의한 정의)
BNF(Backus-Naur Form)와 Context-Free Grammar(문맥 자유 문법)
일단 엄연히 따지자면 BNF와 CFG는 조금 다르다.
BNF
- 창시자: John Backus, 1959
BNF와 context-free grammar는 거의 동일해서 여기서는 CFG를 사용할거라고 한다.
BNF 의 기본 원리

- 구문 구조에 대한 추상화를 쓴다.
ex) <assign> ➡️ <var>=<expression>
- LHS(Left-Hand Side)와 RHS(Right-Hand Side)가 존재한다.
LHS: nonterminal
RHS: string of nonterminals, terminals
- Terminal은 lexeme이나 token이다.
Nonterminal은 <>안에 표현하고, Terminal은 꺾쇠를 안쓴다.
시작 symbol: grammar안의 special nonterminal
가변 길이의 syntatic list 표현하기: recursion을 이용해서!
* recursion: LHS가 RHS에 포함되어 있을 때.
추상화
Derivation(유도)
- sentential form: derivation에 포함된 모든 symbol string
- sentence: terminal symbol만 가지고 있는 sentential form
- leftmost derivation(최좌단유도): sentential form에서 가장 왼쪽의 nonterminal만 expand되는 유도.
Parse Tree
- derivation에 대한 계층적 표현
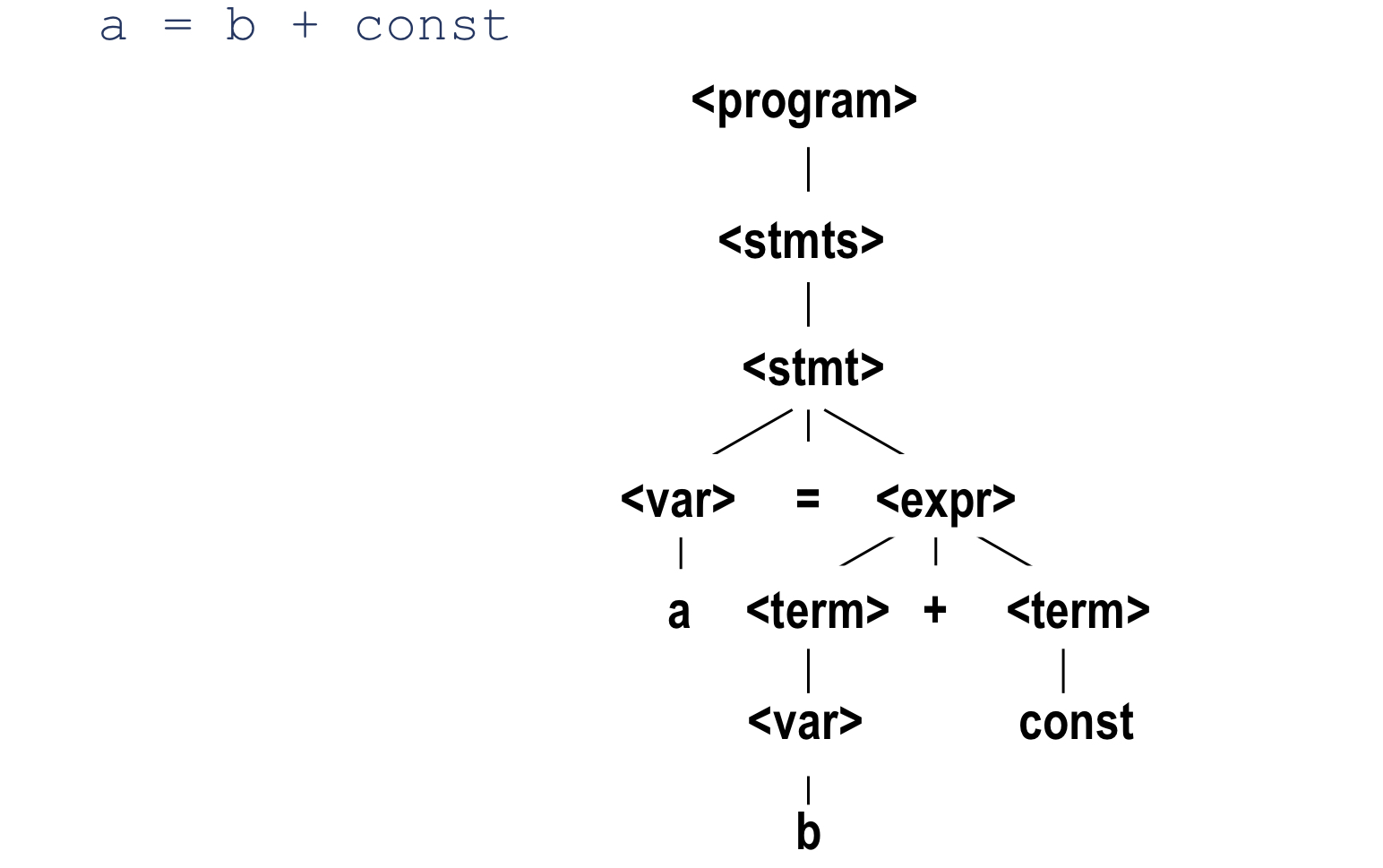
Grammar의 모호성
: 여러개의 parse tree가 생기는 경우.
const-const / const를 표현하고자 할 때, 2개의 다른 tree가 나온다.

컴파일러에서는 parse tree를 이용해서 문장에 대한 소스 코드를 생성하는데, 모호성이 있다면 문제가 발생할 수도 있다.
우선순위 배정해서 모호성 해결하기 - 연산자 우선순위
ex) 나누기가 빼기보다 먼저이다.
연산자 결합 규칙
a+b+c -> (a+b)+c 좌결합법칙(Left-Recursive)
if-then-else를 살펴보자
(if () {} else {}) 와 같다고 생각하면 될 것 같다. )
EBNF

최근의 EBNF 변화들
Attribute Grammar (속성 문법)
Dynamic Semantics
- Axiomatic Semantics
'PL > Programming Language' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [PL] pass by value와 pass by reference (그리고 pass by assignment) (0) | 2021.12.08 |
|---|---|
| [PL][WIP] 파이썬으로 Lexical Analyzer 만들기 (0) | 2021.11.02 |
| [ProgrammingLanguage] 언어 구현하기- Compilation, Pure Interpretation, Hybrid, Preprocessor (0) | 2021.09.10 |
| [ProgrammingLanguage] 폰 노이만 구조, 병목 (0) | 2021.09.10 |
| [ProgrammingLanguage] 언어를 평가하는 기준 (0) | 2021.09.10 |
